APT 038
Suspected attribution: North Korea
Target sectors: Banks worldwide
Associated malware: NETEGG, MACKTRUCK, BLINDTOAD, BOOTWRECK, CHEESTRAY, CLEANTOAD, CLOSESHAVE
Overview: We believe APT38’s financial motivation, unique toolset, and tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) observed during their carefully executed operations are distinct enough to be tracked separately from other North Korean cyber activity. There are many overlapping characteristics with other operations, known as “Lazarus” and the actor we call TEMP.Hermit; however, we believe separating this group will provide defenders with a more focused understanding of the adversary and allow them to prioritize resources and enable defense. The following are some of the ways APT38 is different from other North Korean actors, and some of the ways they are similar:
Associated malware: A diverse suite of malware for initial intrusion and exfiltration. Along with custom malware used for espionage purposes, APT37 also has access to destructive malware.
Attack vectors:
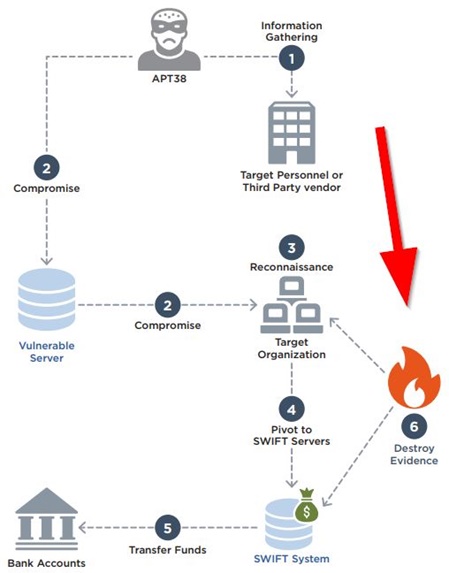
- Information Gathering: Conducted research into an organization’s personnel and targeted third party vendors with likely access to SWIFT transaction systems to understand the mechanics of SWIFT transactions on victim networks (Please note: The systems in question are those used by the victim to conduct SWIFT transactions. At no point did we observe these actors breach the integrity of the SWIFT system itself.).
- Initial Compromise: Relied on watering holes and exploited an insecure out-of-date version of Apache Struts2 to execute code on a system.
- Internal Reconnaissance: Deployed malware to gather credentials, mapped the victim’s network topology, and used tools already present in the victim environment to scan systems.
- Pivot to Victim Servers Used for SWIFT Transactions: Installed reconnaissance malware and internal network monitoring tools on systems used for SWIFT to further understand how they are configured and being used. Deployed both active and passive backdoors on these systems to access segmented internal systems at a victim organization and avoid detection.
- Transfer funds: Deployed and executed malware to insert fraudulent SWIFT transactions and alter transaction history. Transferred funds via multiple transactions to accounts set up in other banks, usually located in separate countries to enable money laundering.
- Destroy Evidence: Securely deleted logs, as well as deployed and executed disk-wiping malware, to cover tracks and disrupt forensic analysis.
IOC's
A public report by Group-IB indicated APT38 logged into watering hole domains associated with (brou.com[.] uy, cnbv.gob[.]mx knf.gov[.]pl) from two IPs (210.52.109.22 and 175.45.178.222) within the same North Korean IP ranges. — A report by Kaspersky indicates APT38 also logged into an Apache Tomcat server used to host its malicious files from the same IP range (175.45.176.0 -175.45.179.255) in January 2017.
| North Korean IP Address Range | Description |
|---|---|
| 175.45.176.0 – 175.45.179.255 | IP range registered to a company in Pyongyang |
| 210.52.109.0 – 210.52.109.255 | IP range registered to a company in China but leased to North Korea |
Used Malware/Tools
| Malware | Description | Detected as |
| BLINDTOAD | BLINDTOAD is 64-bit Service DLL that loads an encrypted file from disk and executes it in memory. |
|
| BOOTWRECK | BOOTWRECK is a master boot record wiper malware. |
|
| CHEESETRAY | CHEESETRAY is a sophisticated proxy-aware backdoor that can operate in both |
|
| CLEANTOAD | CLEANTOAD is a disruption tool that will delete file system artifacts, including those related to BLINDTOAD, and will run after a date obtained from a configuration file. The malware injects shellcode into notepad.exe and it overwrites and deletes files, modifies registry keys, deletes services, and clears Windows event logs. |
|
| CLOSESHAVE | CLOSESHAVE is a secure deletion utility that expects single command line parameter that is a path to an existing file on the system. It overwrites the file with null bytes, changes the file name, and deletes the file. |
|
| DarkComet | DarkComet is a publicly available remote access Trojan (RAT) capable of more than 60 different functions, including collecting system information, controlling all processes currently running on an infected system, viewing and modifying registries, creating a reverse shell, modifying or adding start-up processes and services, keylogging, stealing credentials, recording audio, scanning networks, locking, restarting and shutting down infected systems, updating malware with a new command and control (C&C) server or new functionality, and downloading, modifying, and uploading files. | • Backdoor.DarkComet Trojan.DarkComet • Backdoor.Fynloski • Trojan.Fynloski | ||
| DYEPACK | DYEPACK is a malware suite that manipulates local information regarding SWIFT transaction activity. DYEPACK would most likely be used to cover the traces of fraudulent SWIFT transactions that were performed via other tools or tactics. Variants of this malware may have been intended for deployment within multiple financial institutions targeted by likely related malicious activity. However, its actual deployment has not been confirmed in all of these cases. | • Hacktool.APT.DYEPACK | ||
| DYEPACK.FOX | Variant of DYEPACK utility. DYEPACK.FOX has the ability to manipulate PDF documents containing records of SWIFT messages. | • Hacktool.APT.DYEPACK | ||
| HERMES | HERMES is a multi-threaded ransomware that enumerates all logical drives on a system and starts a new encryption thread for each drive. It attempts to encrypt all files using AES256 encryption that return FILE_ATTRIBUTE_ NORMAL for GetFileAttributes requests. HERMES will attempt to create and display a file on the desktop called DECRYPT_INFORMATION.txt containing the ransom instructions. |
| ||
| HOTWAX | HOTWAX is a module that upon starting imports all necessary system API functions, and searches for a .CHM file. HOTWAX decrypts a payload using the Spritz algorithm with a hard-coded key and then searches the target process and attempts to inject the decrypted payload module from the CHM file into the address space of the target process. |
| ||
| JspSpy | JspSpy is a publicly available web shell that has been posted on github.com. One publicly available version says "Code By Ninty" |
| ||
| KEYLIME | KEYLIME is a keylogger and clipboard logger that encodes the results to a log file. |
| ||
| MAPMAKER | MAPMAKER is a reconnaissance tool that enumerates and prints active TCP connections on the local system. It queries the operating system for the IPv4 TCP connection table, and writes lines like "<ip>:<port> -> <ip>:<port>" to a log file. |
| ||
| NACHOCHEESE | NACHOCHEESE is a command-line tunneler that accepts delimited C&C IPs or domains via command-line and gives actors shell access to a victim's system. |
| ||
| NESTEGG | NESTEGG is a memory-only backdoor that can proxy commands to other infected systems using a custom routing scheme. It accepts commands to upload and download files, list and delete files, list and terminate processes, and start processes. NESTEGG also creates Windows Firewall rules that allows the backdoor to bind to a specified port number to allow for inbound traffic. |
| ||
| QUICKCAFE | QUICKCAFE is an encrypted JavaScript downloader for QUICKRIDE.POWER that exploits the ActiveX M2Soft vulnerabilities. QUICKCAFE is obfuscated using JavaScript Obfuscator. |
|